Introduction
Planetarium projectors are the heart of any planetarium, serving as the primary tool for simulating the night sky and creating immersive astronomical experiences. These sophisticated devices project images of stars, planets, and other celestial bodies onto a dome-shaped screen, allowing audiences to explore the universe from the comfort of their seats. The evolution of planetarium projectors has been remarkable, transitioning from simple optical-mechanical systems to advanced digital technologies that offer stunning visuals and interactive displays.
Components of Planetarium Projectors
A. Optical Systems
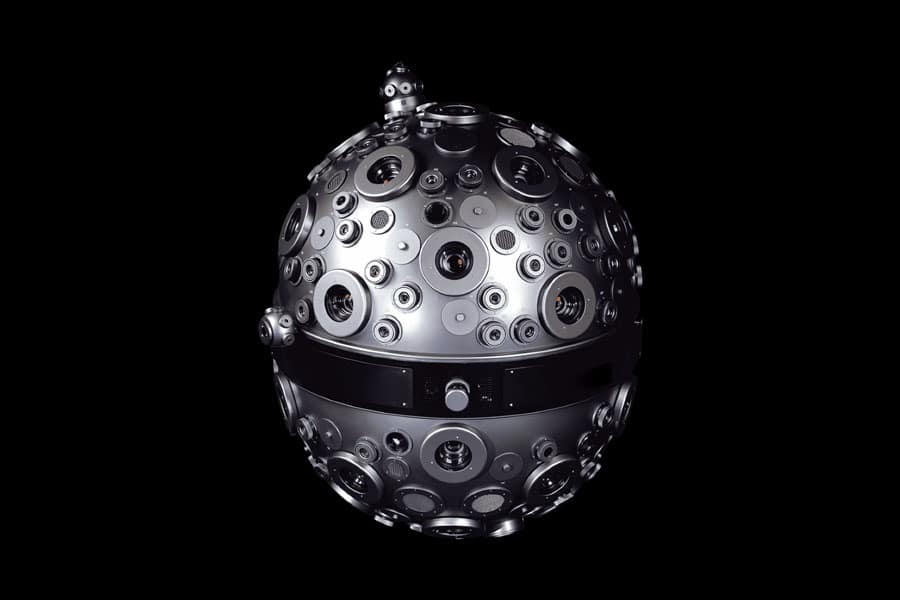
Traditional planetarium projectors relied on optical-mechanical systems, which used lenses, mirrors, and light sources to project images of the night sky. These systems, like the iconic Spitz and Zeiss models, were groundbreaking in their ability to accurately represent celestial movements. However, modern planetariums have largely transitioned to digital projectors, which use advanced imaging technologies to create more dynamic and versatile presentations.
B. Dome and Projection Surface
The dome shape of a planetarium is crucial for creating an immersive viewing experience. Unlike flat screens, dome surfaces provide a 360-degree field of view, enveloping the audience in the projected imagery. This design allows for a more realistic simulation of the night sky, as viewers can look around and feel as though they are truly under the stars.
C. Audio Systems
Sound plays a vital role in enhancing the immersive experience of a planetarium show. High-quality audio systems complement the visual projections, providing narration, music, and sound effects that transport audiences to distant worlds and galaxies.
How Planetarium Projectors Function
A. Light Sources
Planetarium projectors use various light sources to create bright and vivid images. LED and laser technologies are common, offering high brightness levels and long lifespans. These light sources are essential for projecting clear and detailed images onto the dome surface.
B. Image Projection Techniques
The process of projecting images in a planetarium involves complex image projection techniques. Digital projectors use computer-generated imagery to create realistic representations of celestial bodies. These images are then projected onto the dome, often with the help of advanced software that simulates the movement of stars and planets.
C. Control Systems
Dynamic planetarium presentations require sophisticated control systems. Operators use specialized software to program shows, controlling the timing, sequence, and content of the projections. This allows for interactive and engaging presentations that can be tailored to different audiences and topics.
Types of Planetarium Projectors
A. Optical-Mechanical Projectors
Optical-mechanical projectors, such as those made by Spitz and Zeiss, were the first to be used in planetariums. These projectors use a combination of lenses and mechanical components to simulate the night sky. While they are less common today, they are still appreciated for their historical significance and mechanical precision.
B. Digital Projectors
Digital projectors represent the cutting edge of planetarium technology. They offer a wide range of capabilities, including high-resolution imagery, 3D projections, and interactive displays. These projectors are capable of simulating millions of stars and providing highly detailed representations of celestial phenomena.
C. Hybrid Systems
Some planetariums use hybrid systems that combine optical and digital technologies. These systems offer the best of both worlds, providing the mechanical precision of optical projectors with the versatility and interactivity of digital systems.
Applications of Planetarium Projectors
A. Education
Planetarium projectors are invaluable tools for education, particularly in schools and museums. They provide a unique way to teach astronomy, allowing students to explore the universe and learn about celestial phenomena in an engaging and interactive environment.
B. Entertainment
Beyond education, planetarium projectors are used for entertainment purposes. Full-dome movies and immersive experiences captivate audiences, offering a unique form of storytelling that transports viewers to other worlds and galaxies.
C. Research and Community Engagement
Planetariums also play a role in research and community engagement. They serve as venues for public outreach, engaging communities with astronomy and encouraging interest in science and exploration.
Challenges and Innovations
Despite their many benefits, planetarium projectors face challenges, particularly regarding cost and accessibility. Advanced projectors can be expensive to purchase and maintain, limiting their availability to larger institutions. However, ongoing innovations in projection technology, such as increased resolution and interactivity, continue to enhance the capabilities and accessibility of planetarium systems.
Conclusion
Planetarium projectors are essential for modern education and entertainment, providing immersive experiences that inspire and educate audiences about the universe. As technology continues to advance, the future of planetarium projectors holds exciting possibilities, with new trends and innovations set to transform the way we explore the cosmos.
Discover the technology behind planetarium projectors! Contact Virtually Anywhere today to explore how these advanced systems create breathtaking celestial displays, bringing the wonders of the universe to life. Whether for education, entertainment, or research, planetarium projectors make space exploration accessible to all. Start your journey into the stars today!
Frequently Asked Questions (People also ask)
- How do planetarium projectors work?
Planetarium projectors use a combination of optical and digital technologies to project images of celestial bodies onto a dome-shaped screen, creating an immersive experience. - What are the types of planetarium projectors?
There are optical-mechanical projectors, digital projectors, and hybrid systems that utilize both technologies for enhanced presentations. - What is the purpose of a planetarium?
Planetariums serve to educate the public about astronomy and provide entertainment through immersive shows and visual displays of the night sky. - How realistic are planetarium projectors?
Modern projectors can simulate millions of stars and provide a highly detailed representation of the night sky, often using advanced technologies to enhance realism.